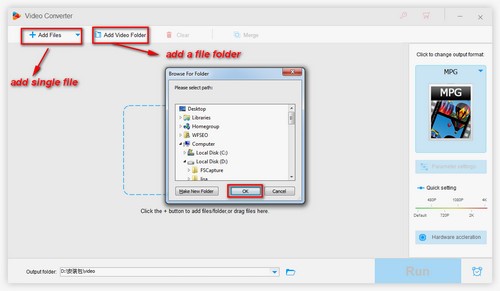
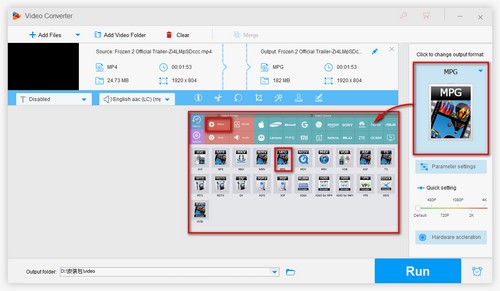
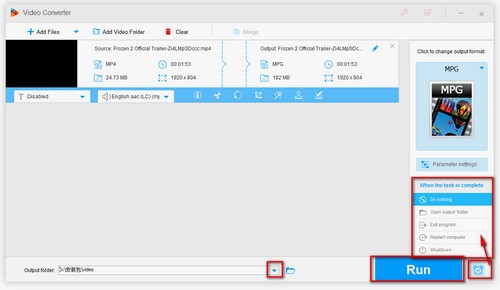
1. MPEG2 vs MPEG4 – Application
The two encoder formats are used this time for various applications. MPEG2 is mainly applied for DVDs and television broadcast, while MPEG4 coding standard mostly for portable devices and Internet streaming. In our daily life, we meet many files encoded by MPEG2 or MPEG4. For example, files with the filename extensions: .mpg, .mpeg, .m2v, .mp2, mp3 are encoded by MPEG4, and .mp4, .m4a, .m4b, .m4r, .m4v for MPEG4.
2. MPEG2 vs MPEG4 - Compression and File Size
The number of bits mainly determines the compression rate of video or audio. Using superior compression algorithm, MPEG4 is much more compressed than MPEG2 while guaranteeing the quality of video. The number of bits also affect the size of file. Thus, the file encoded by MPEG2 is much smaller than that encoded by MPEG4. For instance, a full-length movie file produced by MPEG2 is five times larger than that produced by MPEG4.
3. MPEG2 vs MPEG4 – Quality
MPEG2 less compressing video and audio produces the better quality compared to MPEG4. However, as mentioned above, MPEG2 has larger size than MPEG4, which makes MPEG2 impractical for portable devices or network streaming. Therefore, when you want to stream online, MPEG4 can provide better quality for streaming.
4. MPEG4 vs MPEG2 – Bit Rate & Bandwidth
The bitrate for files encoded by MPEG2 ranges from 50 to 80 Mbits/sec, while MPEG4 has low bitrate video transmission. When you want to stream a video, you will find the video encoded by MPEG2 requires more bandwidth than the MPEG4 video.