When it comes to choosing an audio format, two names frequently arise: WAV and MP3. Both formats are widely used, yet they serve different purposes and audiences. Understanding the key differences between them can help you make informed decisions about which format to use for your specific needs. Next, let's jump in the detailed comparison of WAV vs. MP3.
WAV (Waveform Audio File Format) was developed by Microsoft and IBM as a part of the Resource Interchange File Format (RIFF). It has been around since the early 1990s and is one of the oldest digital audio formats. The file extension for WAV files is typically ".wav".
MP3 (MPEG-1 Audio Layer 3) was developed by the Moving Picture Experts Group (MPEG) and became popular in the mid-1990s. It revolutionized the music industry by enabling efficient storage and transmission of audio files. MP3 files basically use ".mp3" as the file extension.
WAV files are typically uncompressed and not subject to licensing restrictions, making them a preferred choice for professional audio recording and editing.
MP3 files were initially subject to patents, but these patents have expired. Despite this, the format remains widely used due to its balance of quality and file size.
WAV files are uncompressed and typically store audio in lossless, CD-quality format. They usually have a bitrate of 1,411 kbps for stereo audio at 44.1 kHz sampling rate, which is considered the standard for CD-quality sound.
MP3, in contrast, uses lossy compression to reduce file size. It supports various bitrates, typically ranging from 128 kbps to 320 kbps. Higher bitrates in MP3 files generally mean better sound quality, with 320 kbps being the highest quality MP3 format. However, even at its highest bitrate, MP3 still compresses audio data and loses some information in the process.
The difference between WAV and MP3 quality is most noticeable in complex audio with a wide frequency range, such as classical music or high-fidelity recordings. For casual listening, while high-bitrate MP3s can sound very good, they do not match the quality of uncompressed WAV files.
WAV files are uncompressed, meaning they retain all audio data and therefore have larger file sizes, while MP3 files use lossy compression, significantly reducing file size by removing certain audio frequencies that are less perceptible to the human ear.
File size is where MP3 really shines. The primary purpose of MP3 was to reduce file sizes while maintaining acceptable audio quality. An MP3 file can be up to 10 times smaller than its WAV counterpart, making it ideal for storage and transmission over the internet.
For example, a 3-minute song in WAV format might be around 30 MB, while the same song as an MP3 at 320 kbps would be about 7 MB. This significant difference in WAV vs MP3 file size has made MP3 the go-to format for portable music players and online music distribution.
Both WAV and MP3 formats support metadata, but MP3 has a more robust and standardized system.
MP3 uses ID3 tags, which can store information like the song title, track number, artist, album, year, genre, and even album artwork. This makes it easy to organize and display information about your music collection.
WAV files can also include metadata, but support is more limited and less standardized. This can lead to inconsistencies in metadata handling across different software and devices.
WAV files are compatible with a wide range of devices and software, particularly within professional audio and video production environments. However, their large size can be a limitation for consumer applications.
MP3 has a slight edge due to its ubiquity. Almost every device and software that can play audio will support MP3 files. This makes MP3 the preferred format for consumer audio and music sharing.
The choice between WAV and MP3 often comes down to the intended use of the audio file. WAV is preferred in professional audio production, recording, and editing due to its lossless quality. It's the format of choice for audio engineers, musicians, and producers who need to maintain the highest possible audio quality throughout the production process.
MP3, on the other hand, is the king of consumer audio. Its small file size and good-enough quality for most listeners have made it the dominant format for music distribution, podcasts, and online streaming. When considering MP3 or WAV for everyday listening, most people opt for MP3 due to its convenience and space-saving benefits.
Pros:
Cons:
Pros:
Cons:
The question "Is MP3 better than WAV?" doesn't have a straightforward answer. It depends entirely on your needs. If you're a professional working with audio or an audiophile who demands the highest quality, WAV is undoubtedly better. Its lossless nature ensures you're working with or listening to the full, uncompressed audio.
However, for everyday listening, music collections, and online distribution, MP3 is often the more practical choice. The difference between MP3 and WAV in terms of perceived sound quality is minimal for most listeners, especially when using high-bitrate MP3s 320kbps.
In the debate of WAV vs MP3 sound quality, WAV wins on a technical level. But when considering factors like storage space, transmission speed, and compatibility, MP3 often comes out on top for consumer use.
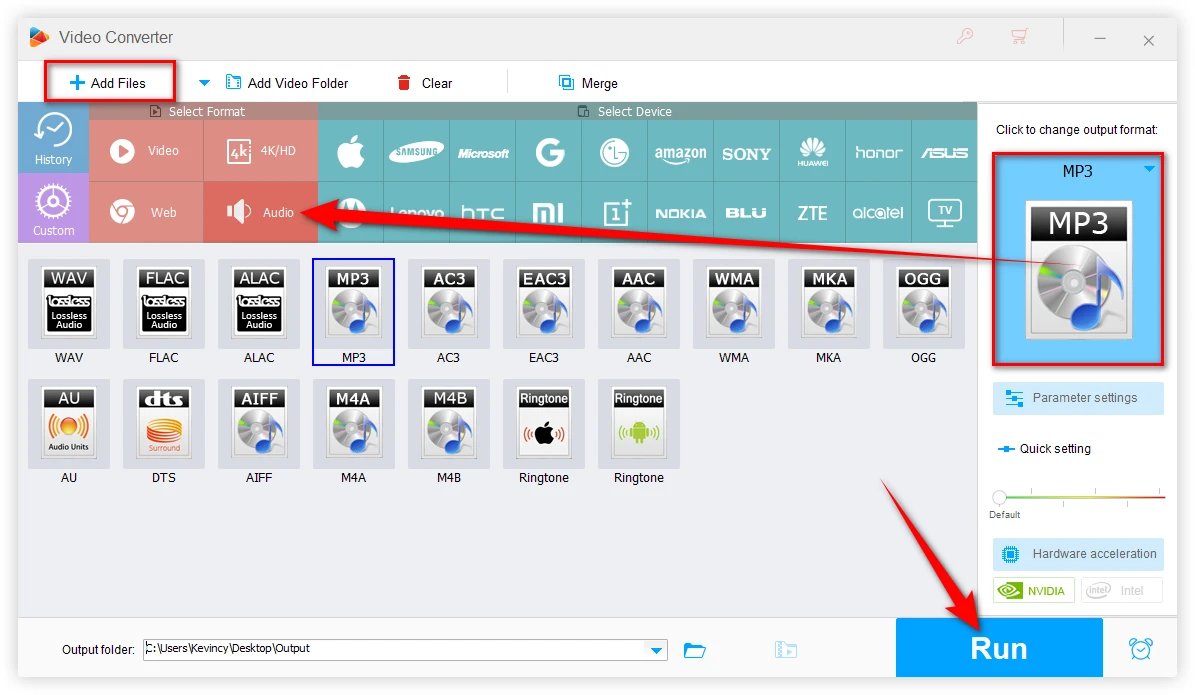
Format conversion is a common requirement. Tools like WonderFox HD Video Converter Factory Pro provide a batch conversion solution, allowing you to switch between WAV and MP3 as needed.
A: In terms of audio quality, yes, WAV files are better because they are uncompressed. However, MP3 files are more convenient for everyday use due to their smaller size and universal compatibility.
A: WAV offers higher quality than MP3, even at 320kbps. However, the difference may be imperceptible to many listeners, especially on consumer-grade audio equipment.
A: MP3 is better for streaming music due to its smaller file size and good audio quality. It allows for faster streaming and less bandwidth usage compared to WAV files.
WonderFox
HD Video Converter Factory Pro
Terms and Conditions | Privacy Policy | License Agreement | Copyright © 2009-2025 WonderFox Soft, Inc. All Rights Reserved.